I. Common Materials
The performance of optical prisms depends heavily on the optical and mechanical properties of the materials. Common materials include:
| Material Type | Characteristics & Applications |
|---|---|
| K9 Optical Glass | Refractive index 1.5168 @589.3nm, cost-effective, widely used in visible spectrum (e.g., laser pointers, educational instruments). |
| Fused Silica | UV-NIR transmission (185nm-2.1μm), low thermal expansion, suitable for high-power laser systems (e.g., CO₂ laser cutting heads). |
| N-BK7 Optical Glass | Low bubble impurities, high homogeneity, ideal for precision imaging systems (e.g., microscope objectives, telescopes). |
| Calcium Fluoride (CaF₂) | High UV/IR transmission (0.15μm-8μm), low dispersion, used in deep UV lithography and IR spectrometers. |
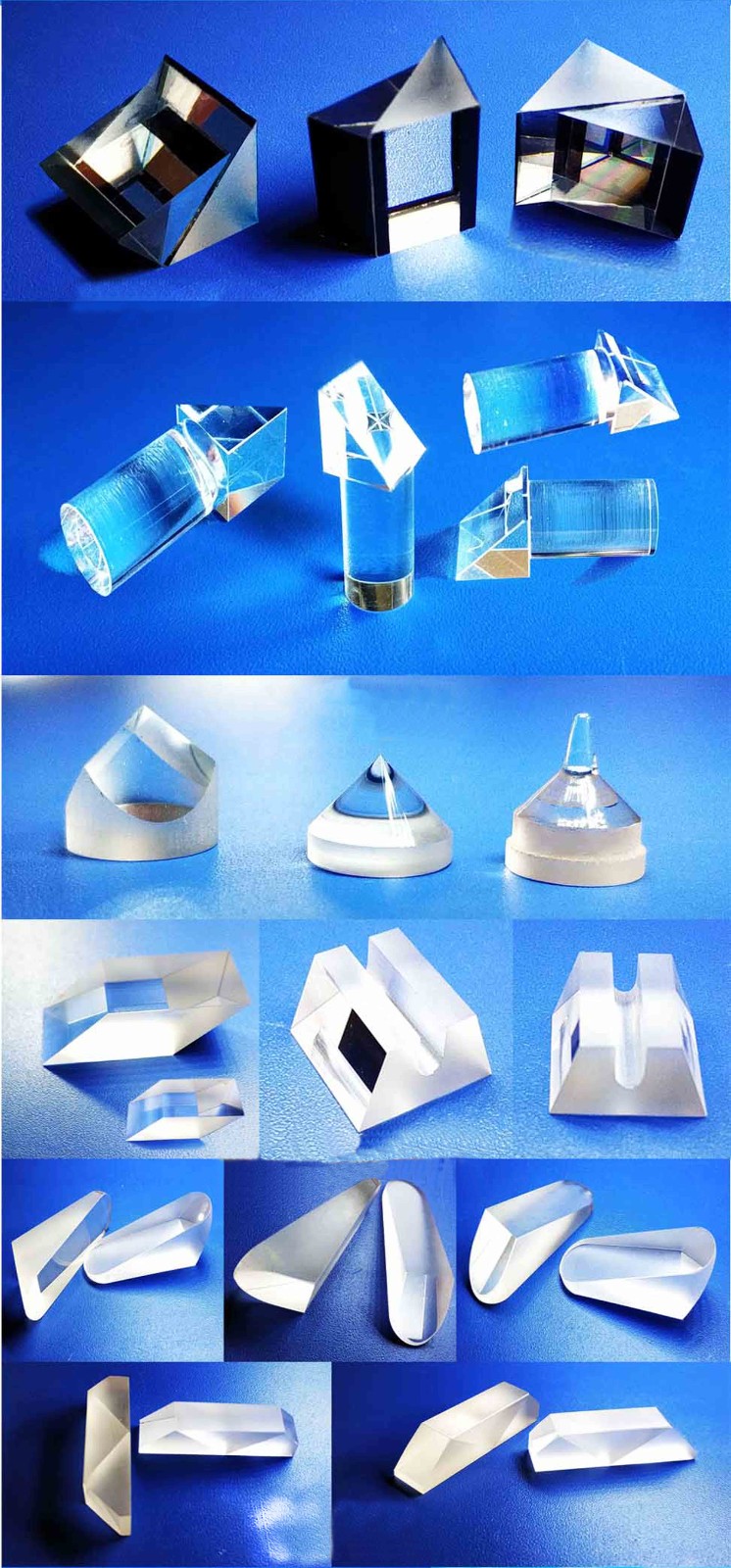
II. Structural Shapes & Functions
Prism shapes determine optical behavior. Common types and functions:
| Type | Structural Features | Core Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Right-Angle Prism | 90° triangular shape, total internal reflection on hypotenuse | 90° beam deflection, image rotation (e.g., laser engraver light path folding). |
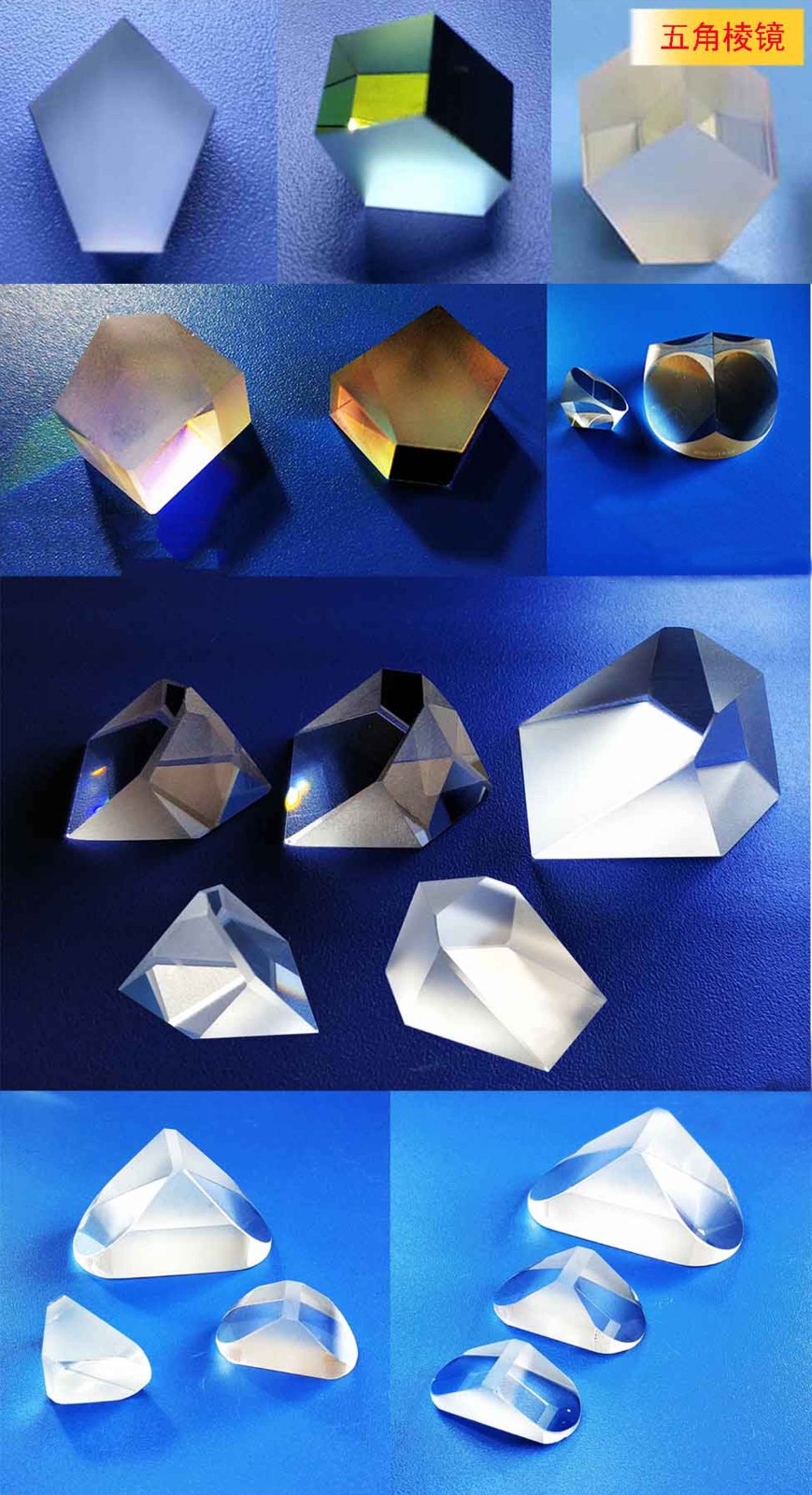
| Pentagonal Prism | Five-sided structure with two reflections | Constant 90° deflection independent of input angle (e.g., rangefinders, military targeting systems). |
| Rhomboid Prism | Parallelogram cross-section | Beam displacement without angular deviation (e.g., interferometer path compensation). |
| Roof Prism | Right-angle prism with roof-shaped reflecting surfaces | Image inversion + beam steering (e.g., binocular image correction). |
| Beamsplitter Prism | Hypotenuse coated with beamsplitting film | Proportional beam energy division (e.g., laser splitting, 3D sensing). |
III. Machining Accuracy Requirements
Prism performance is directly influenced by machining precision. Key parameters include:
1. Geometric Accuracy
◦ Dimensional Tolerance: ±0.01mm (up to ±0.005mm for high-precision applications)
◦ Angular Deviation: <3 arcmin (military-grade: <1 arcmin; 1 arcmin = 1/60 degree)
◦ Surface Flatness: λ/8 @632.8nm (λ = laser wavelength)
2. Surface Quality
◦ Scratch-Dig Standard: 20-10 (scratch width ≤20μm, dig diameter ≤0.1mm)
◦ Roughness: Ra<1nm (ultra-smooth surfaces for UV laser systems)
3. Coating Requirements
◦ Anti-Reflective (AR) Coating: Single-wavelength residual reflectance <0.2%, broadband (400-700nm) residual reflectance <0.5%
◦ High-Reflective (HR) Coating: Reflectance >99.8%@specific wavelengths (e.g., 1064nm lasers)
IV. Core Optical Properties
1. Refraction & Dispersion
◦ Refractive Index (n): Determines beam deflection angle (e.g., K9 glass with n=1.517 produces 28° refraction angle at 45° incidence).
◦ Abbe Number (Vd): Measures dispersion strength; higher Vd = lower dispersion (N-BK7: Vd=64.2).
2. Total Internal Reflection
◦ Critical Angle Formula: θ_c = arcsin(n2/n1), used in right-angle prisms for efficient beam steering.
3. Polarization Properties
◦ Brewster Angle Design: Eliminates reflective polarization loss (e.g., Brewster windows in laser cavities).
4. Beamsplitting Properties
◦ Adjustable Splitting Ratio: 50:50 (equal splitting) or custom ratios (e.g., 80:20 energy distribution).
V. Typical Applications in Optics
Application Field Usage Scenarios & Prism Types
Laser Technology - Beam expansion: Prism pairs (e.g., Nd:YAG laser processors)
- Pulse compression: Fused silica prism pairs (femtosecond lasers).
Imaging Systems - Image correction: Roof prisms (DSLR viewfinders)
- Confocal scanning: Polygonal scanning prisms (biological microscopes).
Spectral Analysis - Dispersion: Constant deviation prisms (Raman spectrometers)
- Wavelength selection: Beamsplitter prisms (fluorescence detectors).
Fiber Optics - Optical coupling: Right-angle prisms (fiber collimators)
- WDM: Coated beamsplitter prisms (DWDM modules).
Precision Metrology - Interferometry: Cube beamsplitter prisms (laser interferometers)
- Angular reference: Pentagonal prisms (aerospace attitude calibration).
Medical Devices - Endoscopic imaging: Micro prism arrays (electronic endoscopes)
- Laser therapy: High LIDT prisms (ophthalmic femtosecond lasers).
The above descriptions serve as a foundational framework for product specifications. Customize with actual test data (e.g., interferometer reports, laser-induced damage threshold results) and industry certifications (ISO 10110 optical drawing standards).



Tel:+86-87895949
Fax :+86-87895949
Mobile:+86-13773518883
E-mail: lens@lens-cn.com
Whatsapp: +86-13773518883

